

Only men had significant differences in path angle between the 4 and 8 m beep distances (4.8° vs 2.9°), occurring as early as the 2nd epoch. The results showed an interaction between beep distance, epoch, and gender. Predicted scaling of the actual 3° target angle is 4.5° for a 4m beep and 2.3° for an 8m beep. Auditory signals are decomposed into discrete frequency elements early in the transduction process, yet somehow these signals are recombined into the rich acoustic percepts that we readily identify and are familiar with. If subjects used the auditory cue for calibration, their angular path to target should scale with beep distance. Distance of beep (4 or 8 m) was tested in blocks of 18 trials, and data were analyzed in 3 time epochs.

A beep, indicating end of trial, was emitted when the subject passed a certain distance. The ball was 3° left or right of starting position, and the task was to walk to the ball. Using VR, 5 men and 5 women saw a 1-s display of a scene with a ball in a doorway located 6 m away. Here we test this hypothesis by varying the distance at which a beep is emitted. We postulate that the men used the implicit auditory cue to calibrate their action system. Over time, men's paths were less affected by scene context. The mole cricket (Gryllolalpa vineae) increases its acoustically effective size by digging a double conical horn-shaped burrow, in which it sings. This is directly related to the size of the sound-producing organ, and therefore of the animal.
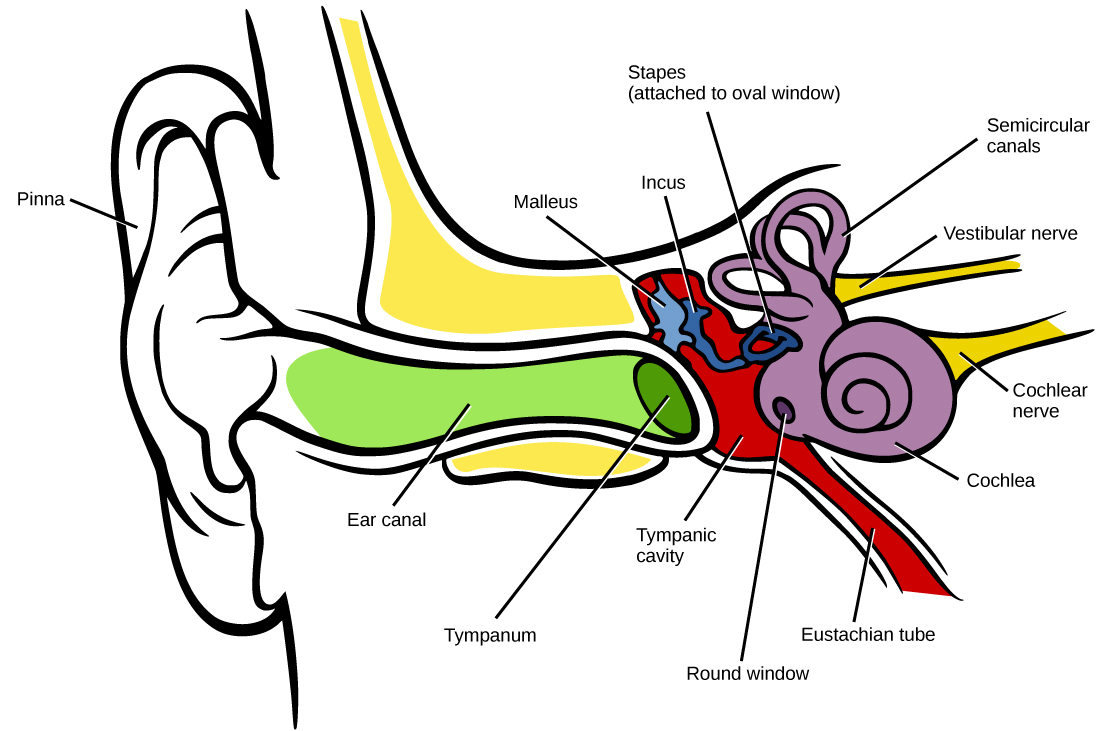
Information travels from the receptors in the organ of Corti of the inner ear the cochlear hair. Initially, paths varied with the changing scene context, indicating a reliance on the memory of non-motion-generated visual information to define an egocentric position. A limit to the effective distance of auditory signals is the loudness that the signaller can achieve. The auditory pathway conveys the special sense of hearing. The only external source capable of providing feedback was a beep emitted at the end of a trial, implicitly signaling target distance. In that experiment, subjects walked without vision to a target in a VR scene. We recently showed that the calibration established in the real world is inoperative in novel immersive virtual environments (VR).
AUDITORY SIGNAL PATH UPDATE
The calibration is stored and can be used to update an accurate egocentric representation of space when external sensory information is absent. As we move we generate changes in the internal and external sensory signals, and the coupling between the two types of signals calibrates our actions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
